
A copy of the Earth and Space sections of
the K-6 and 7-10 NSW Science syllabuses
can be found here.
From the K-6 Syllabus:
“The Earth and Space strand explores the Earth’s dynamic structure and its place in the universe. Students explore changes on Earth, such as day and night, and the seasons related to Earth’s rotation and its orbit around the Sun.
Students investigate the processes that result in changes to the Earth’s surface. They explore the ways in which we use Earth’s resources and consider the influence of human activity on the Earth’s surface and its atmosphere.”
From the 7-10 Syllabus:
“The Earth and Space strand is concerned with the Earth’s dynamic structure and its place in the cosmos. The key concepts developed within this strand are that the Earth is part of a solar system that, in turn, is part of a larger universe and that the Earth is subject to change within and on its surface, over a range of timescales, as a result of natural processes. Students explore the ways that humans use resources from the Earth and appreciate the influence of human activity on the surface of the Earth and the atmosphere.”

Early Stage 1: Changes in the Environment
How do daily and seasonal changes affect the environment?
Key Concepts: Day and Night, Weather, Behaviour

Stage 1: Changes in the Sky and on the Land
How can we investigate the observable changes that occur in the sky and on the land?
Key Concepts: Sun, Moon, Weather, Seasons

Stage 1: Earth’s Resources
What are Earth’s resources and how do we use and care for them?
Key Concepts: Water, Soil, Plants and Animals, Sustainability

Stage 2: How the Earth’s Surface Changes Over Time
How do natural processes and human actions change the Earth’s surface over time?
Key Concepts: Soil, Landforms, Rocks, Fossils, Erosion, Human Activity
Stage 2: Earth’s Relationship with the Sun
What occurs as a result of the interactions between the Earth and the Sun?
Key Concepts: Sun, Energy, Rotation, Orbit, Calendar
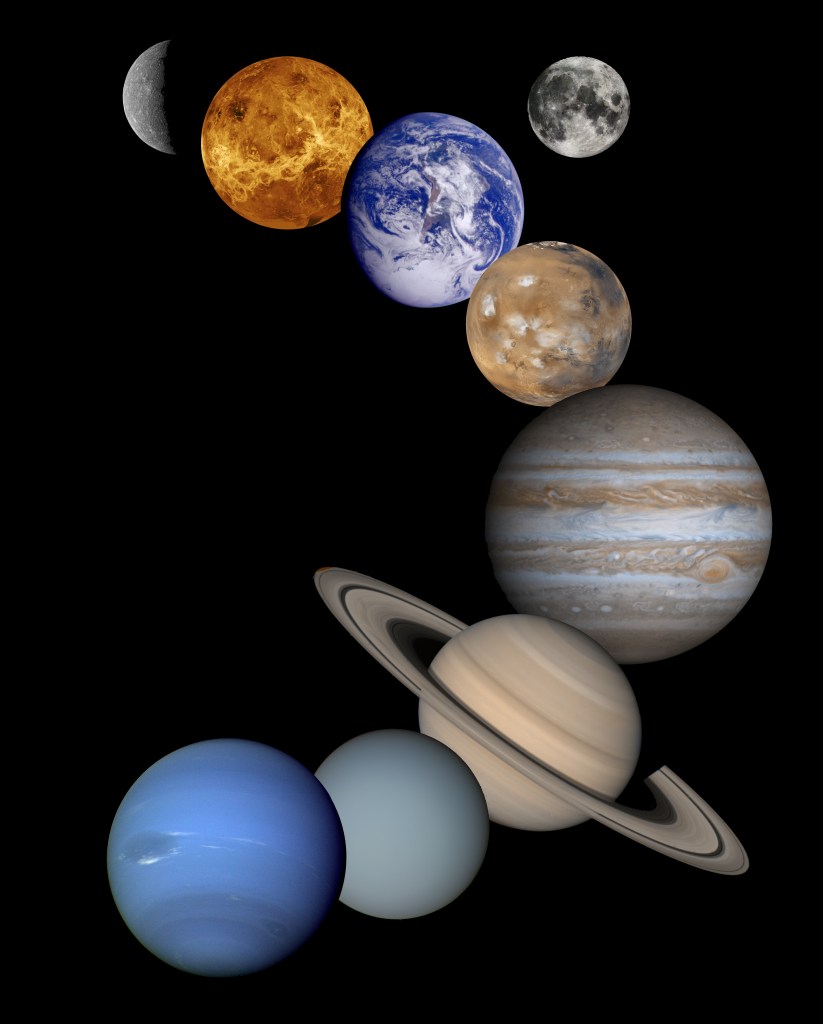

Stage 3: Earth’s Place in our Solar System
How does the Earth compare to other planets in the solar system?
Key Concepts: Solar System, Planets, Star, Light Energy, Orbit, Size and Distance, Night Sky Observation, Astronomy
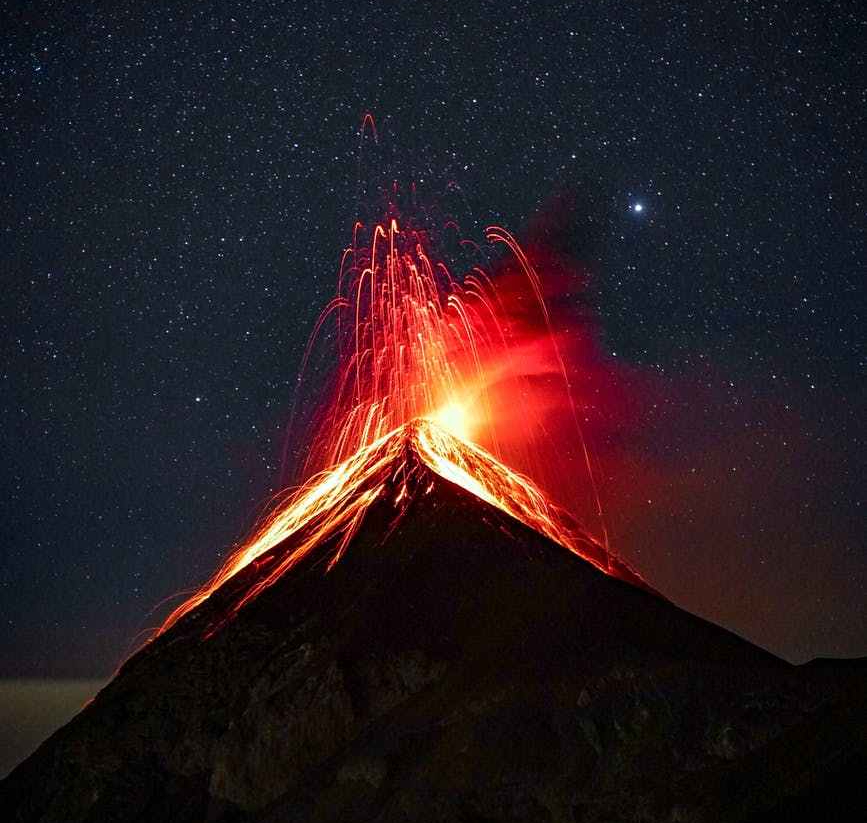

Stage 3: Changes to Earth’s Surface
How do sudden geological changes and extreme weather events affect the Earth’s surface?
Key Concepts: Geological Change, Earthquakes, Volcanic Eruptions, Tsunamis, Cyclones, Storms, Drought, Floods, Natural Disaster Technologies
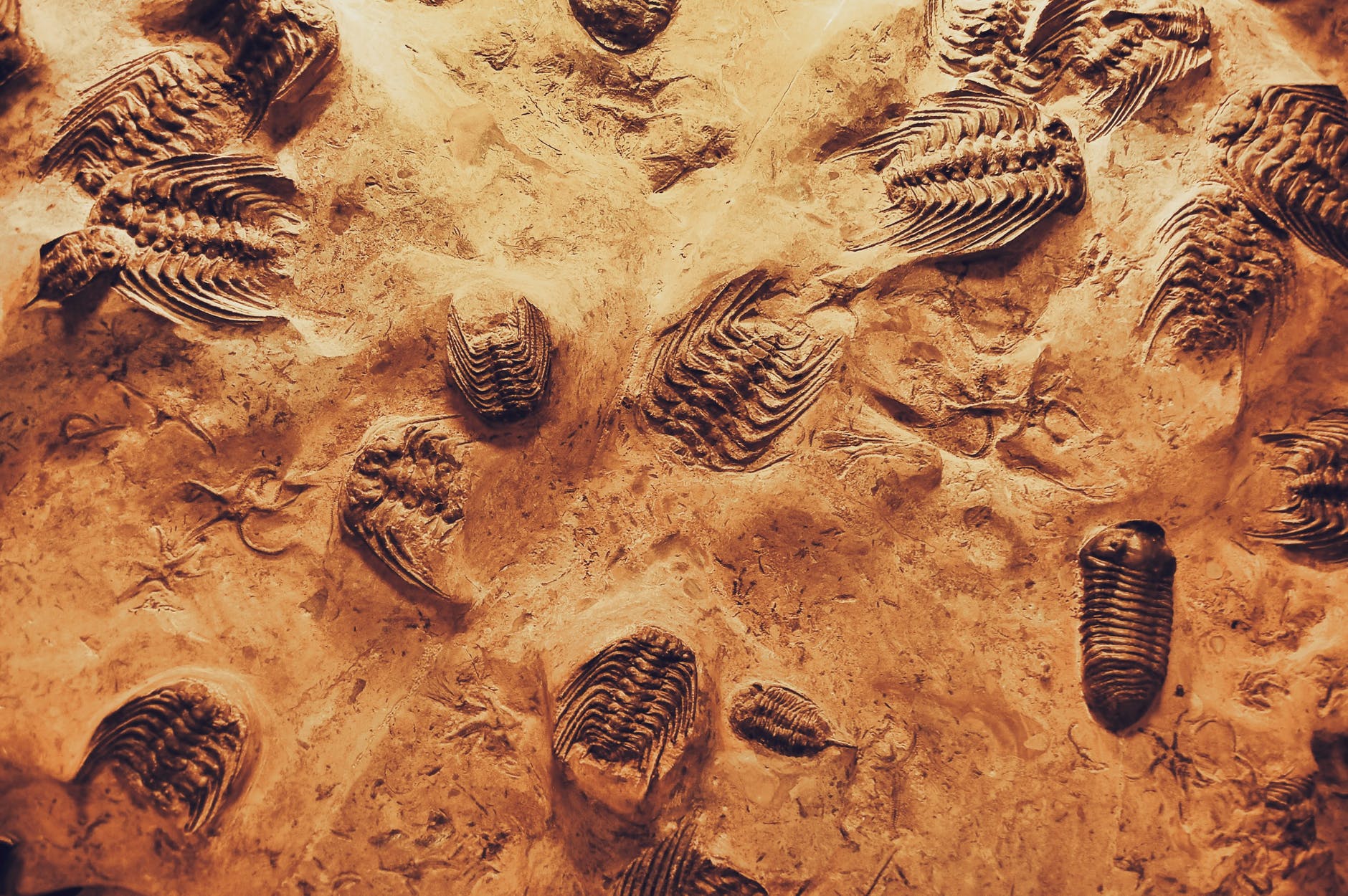

Stage 4: Sedimentary, Igneous & Metamorphic Rocks (Fossils)
Sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks contain minerals and are formed by processes that occur within Earth over a variety of timescales.
Key Concepts: Earth Structure, Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, Sedimentary, Igneous, Metamorphic, Minerals, Fossils, Geologic History, Mining

Scientific knowledge changes as new evidence becomes available. Some technological developments and scientific discoveries have significantly changed people’s understanding of the solar system.
Key Concepts: Day and Night, Seasons, Eclipses, Solar System, Models, Technological Advancements (Astronomy)
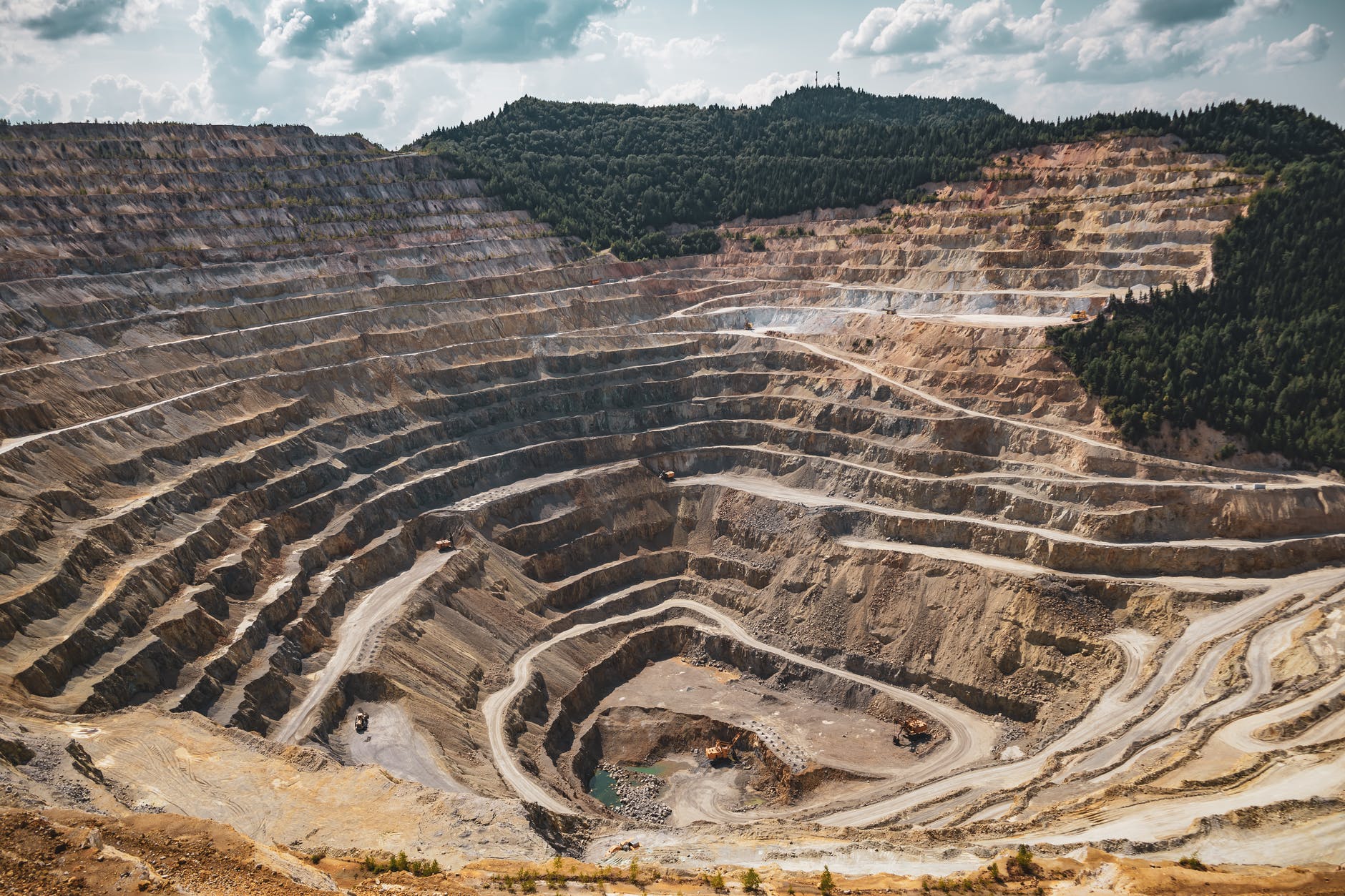

Stage 4: Use and Management of the Earth’s Resources
Scientific knowledge influences the choices people make in regard to the use and management of the Earth’s resources.
Key Concepts: Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources, Ores, Fossil Fuels, Earth’s Spheres

Science understanding influences the development of practices in areas of human activity such as industry, agriculture and marine and terrestrial resource management.
Key Concepts: Water Cycle, Household, Industry, Agriculture, Resource Management

Stage 4: Additional Content
Key Concepts: Collaboration, Forces (Sun, Moon), Rock and Mineral Formation, Rock Layers, Mining

Scientific understanding, including models and theories, are contestable and are refined over time through a process of review by the scientific community.
Key Concepts: Galaxies, Stars, Solar Systems, Nebulae, Technology (Astronomy), Scale, Gravity, Big Bang Theory

The theory of plate tectonics explains global patterns of geological activity and continental movement.
Key Concepts: Plate Tectonics, Continental Movement, Earthquakes, Volcanic Activity, Landform Formation

People use scientific knowledge to evaluate claims, explanations or predictions in relation to interactions involving the atmosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere.
Key Concepts: Earth’s Spheres, Carbon Cycle, Natural Events, Greenhouse Effect, Ozone Layer Depletion, Climate Change, Waste Management, Loss of Biodiversity

Stage 5: Additional Content
Key Concepts: Stars, Age of the Universe, El Nino and La Nina, Deep Ocean Currents, Atmospheric Pollution, Ocean Salinity, Climate Change, International Agreements, Science Careers
